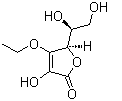
DESCRIPTION
3-O-ethyl ascorbic acid is a new generation of Vitamin C derivative that provides superb whitening effects, also serves as a potent anti-aging active that boosts collagen synthesis and protects skin from DNA damage. It exhibits strong inhibition effect on melanogenesis, reduces dark spots and age spots, fights photoaging by interfering with inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6, and reverse ROS production to achieve free radical scavenging purpose. 3-O-ethyl ascorbic acid is effectively a newer form of Vitamin C that offers a better overall performance. It is water soluble with excellent heat and photostability profile. Best of all, it is highly stable and easy to formulate. |
PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
∙ | Anti-Oxidation | |
∙ | Anti-photoageing (Reduce IL-6) | |
∙ | Inhibit Tyrosinase and Trp-2 Activities (whitening) | |
∙ | Even Out Skin Tone | |
∙ | Stimulate Collagen Synthesis | |
∙ | Reduce Dark Spots (depigmenting) | |
∙ | Protect DNA | |
∙ | Scavenge Free Radicals | |
Anti-aging |
REGULATION
INCI name: 3-O-Ethyl Ascorbic Acid
|
SPECIFICATIONS / CONDITIONS OF USE
Appearance | : | white to off-white crystalline powder |
Melting point (°C ) | : | 111.0-116.0 |
Water Content | : | ≤ 1.0% |
pH (3% water solution) | : | 4.0-5.5 |
Heavy metals | : | ≤ 20ppm |
Arsenic | : | ≤ 2ppm |
Ash | : | ≤0.1% |
Assay (HPLC) | : | ≥ 98.5% |
Free Vc (HPLC) | : | ≤10ppm |
Total plate count | : | ≤500cfu/g |
DOSAGE
% utilization | 0.5 - 2% |
Formulation Guide | 3-O-ethyl ascorbic acid is much stable at a pH range between 5-6.5. It is recommended that dissolve 1g 3-O-ethyl ascorbic acid in 1g citric acid buffer (pH 5.5) and then add to water phase.
| |||||||||||||||
Storage Conditions | Protect from contacting with light, heat and moisture. |
Table 1 Stability and antioxidative of 3-O-ethyl ascorbic acid, ascorbic acid and Magnesium ascorbyl phosphate
Thermal Stability | Antioxidative Activity [The scavenging activity of 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical] | ||
Retaining rate( 6 weeks at 60°C in aq. solution) | Radical-scavenging activity (IC50 value ) | DPPH radical scavenging amount | |
3-O-ethyl ascorbic acid | 95.5% | 10.35µg | 2.29 g·g-1 |
Magnesium ascorbyl phosphate | 70.6% | 163.44µg | 0.15 g ·g- |
Ascorbic Acid | <0.01% | 8.42µg | 2.82g·g-1 |
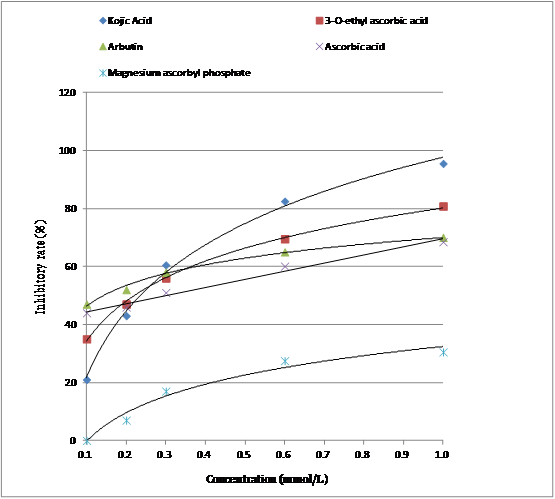
Fig 1. Plots of concentration vs. inhibitory activity against tyrosinase-catalyzed oxidation of L-tyrosine.
The inhibitory rate of 3-O-ethyl ascorbic acid on tyrosinase activity in oxidizing L-tyrosine into melanin achieves 80.0%, which is lower than that of kojic acid (inhibitory rate 95.5%), but higher than ascorbic acid (inhibitory rate 68.5%)
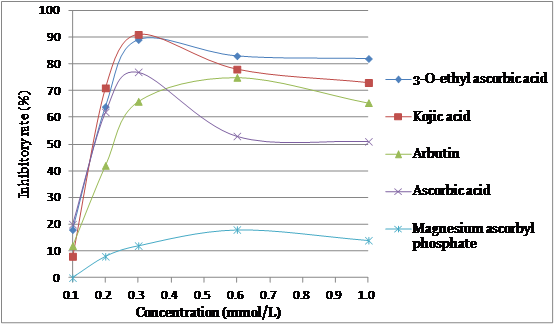
Fig. 2 Plots of concentration vs. inhibitory activity against tyrosinase - catalyzed oxidation of L-dopa. Activity of 3-O-ethyl ascorbic acid against capacity of tyrosinase to oxidize L-dopa forming melanin achieves 89.1%. The inhibitor concentration causing 50% loss of activity (IC50 value) is 0.15mmol/L
Documentation:

